The AsyncTask class is used to perform background tasks and it might be useful to show notifications and progress bars to alert the user.
In this post I write an example where I create two AsyncTask instances showing a startup notification, a progress bar and a notification of completed task
-
- the MainActivity class, the main activity
package eu.lucazanini.asynctaskandnotifications; import android.annotation.TargetApi; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.AsyncTask; import android.os.Build; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; public class MainActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); Button btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @TargetApi(11) private void asyncTaskApi11() { new NotificationTask(getApplicationContext(), "Job one", 1) .executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR, 10); new NotificationTask(getApplicationContext(), "Job two", 2) .executeOnExecutor(AsyncTask.THREAD_POOL_EXECUTOR, 5); } @Override public void onClick(View v) { if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) { new NotificationTask(getApplicationContext(), "Job one", 1) .execute(10); new NotificationTask(getApplicationContext(), "Job two", 2) .execute(5); } else { asyncTaskApi11(); } } }); } }when you click the button inside the layout you create two AsyncTask instances, if the API version is less than 11 (HONEYCOMB) the AsyncTask instances are launched with the execute() method otherwise with the executeOnExecutor() method available from API version 11.
It is better to launch the AsyncTask using the executeOnExecutor() method because in this way they are executed at the same time and it is more obvious what I want to show. - the NotificationTask class extending AsyncTask
- the MainActivity class, the main activity
package eu.lucazanini.asynctaskandnotifications;
import android.app.NotificationManager;
import android.app.PendingIntent;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.support.v4.app.NotificationCompat;
import android.support.v4.app.TaskStackBuilder;
import android.util.Log;
public class NotificationTask extends AsyncTask<Integer, Double, Void> {
private final static String TAG = NotificationTask.class.getName();
private NotificationCompat.Builder mBuilder;
private final Context mContext;
private final int mId;
private NotificationManager mNotifyManager;
private final String mTitle;
public NotificationTask(Context context, String title, int id) {
mContext = context;
mTitle = title;
mId = id;
}
@Override
protected Void doInBackground(Integer... params) {
Log.d(TAG, "doInBackground");
// waiting 3 seconds so you can see the first notification
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getMessage());
}
// the long job
try {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long startTime = currentTime;
long endTime = startTime + (params[0] * 1000);
long lastTime = currentTime;
double totalTime = endTime - startTime;
publishProgress(0D);
while (currentTime < endTime) {
if (currentTime > lastTime + 100) {
double perc = (currentTime - startTime) / totalTime * 100D;
publishProgress(perc);
lastTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
Thread.sleep(10);
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
publishProgress(100D);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
/**
* called only once
*/
private void initNotification() {
mNotifyManager = (NotificationManager) mContext
.getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
mBuilder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(mContext);
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Void result) {
Log.d(TAG, "onPostExecute");
super.onPostExecute(result);
// createNotification("completed");
setCompletedNotification();
}
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
Log.d(TAG, "onPreExecute");
super.onPreExecute();
initNotification();
setStartedNotification();
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Double... values) {
Log.d(TAG, "onProgressUpdate with argument = " + values[0]);
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
int incr = values[0].intValue();
if (incr == 0)
setProgressNotification();
updateProgressNotification(incr);
}
/**
* the last notification
*/
private void setCompletedNotification() {
mBuilder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher).setContentTitle(mTitle)
.setContentText("Completed");
// Creates an explicit intent for an Activity in your app
Intent resultIntent = new Intent(mContext, ResultActivity.class);
// The stack builder object will contain an artificial back stack for
// the
// started Activity.
// This ensures that navigating backward from the Activity leads out of
// your application to the Home screen.
TaskStackBuilder stackBuilder = TaskStackBuilder.create(mContext);
// Adds the back stack for the Intent (but not the Intent itself)
stackBuilder.addParentStack(MainActivity.class);
// Adds the Intent that starts the Activity to the top of the stack
stackBuilder.addNextIntent(resultIntent);
PendingIntent resultPendingIntent = stackBuilder.getPendingIntent(0,
PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
mBuilder.setContentIntent(resultPendingIntent);
mNotifyManager.notify(mId, mBuilder.build());
}
/**
* the progress notification
* <p>
* called only once
*/
private void setProgressNotification() {
mBuilder.setContentTitle(mTitle).setContentText("Download in progress")
.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher);
}
/**
* the first notification
*/
private void setStartedNotification() {
mBuilder.setSmallIcon(R.drawable.ic_launcher).setContentTitle(mTitle)
.setContentText("Started");
// Creates an explicit intent for an Activity in your app
Intent resultIntent = new Intent(mContext, MainActivity.class);
// The stack builder object will contain an artificial back stack for
// the
// started Activity.
// This ensures that navigating backward from the Activity leads out of
// your application to the Home screen.
TaskStackBuilder stackBuilder = TaskStackBuilder.create(mContext);
// Adds the back stack for the Intent (but not the Intent itself)
stackBuilder.addParentStack(MainActivity.class);
// Adds the Intent that starts the Activity to the top of the stack
stackBuilder.addNextIntent(resultIntent);
PendingIntent resultPendingIntent = stackBuilder.getPendingIntent(0,
PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
mBuilder.setContentIntent(resultPendingIntent);
mNotifyManager.notify(mId, mBuilder.build());
}
/**
* the progress notification
* <p>
* called every 0.1 sec to update the progress bar
*
* @param incr
*/
private void updateProgressNotification(int incr) {
// Sets the progress indicator to a max value, the
// current completion percentage, and "determinate"
// state
mBuilder.setProgress(100, incr, false);
// Displays the progress bar for the first time.
mNotifyManager.notify(mId, mBuilder.build());
// Sleeps the thread, simulating an operation
// that takes time
}
}
there are three overidden methods:
-
-
- onPreExecute(): here I initialize the notifications, especially I set the id passed to the constructor (line 163), then the two AsynTask instances have id equal to 1 and 2
- doInBackground(Integer… params): I wait 3 seconds and after I display the progress bar, in the first AsyncTask instance the time is 10 seconds, in the second one it is 5 seconds, these values are set as argument in the execute() or executeOnExecutor() methods.
- onPostExecute(Void result): the notification “completed” opening the ResultActivity
-
- the ResultActivity class displayed when the user click on the notification “completed”
package eu.lucazanini.asynctaskandnotifications; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; public class ResultActivity extends Activity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_result); } } - AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="eu.lucazanini.asynctaskandnotifications" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0" > <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="19" /> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/AppTheme" > <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name" > <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <activity android:name=".ResultActivity" /> </application> </manifest> - the layouts, very easy
- res/layout/activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <Button android:id="@+id/button1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Start" /> </LinearLayout> - res/layout/activity_result.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" > <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="This activity is called by notification" /> </LinearLayout>
- res/layout/activity_main.xml
The following are the screen shots of the app, note that the notifications are split according to the id.
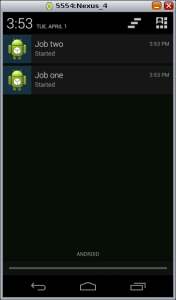
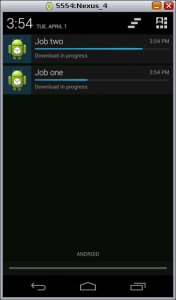
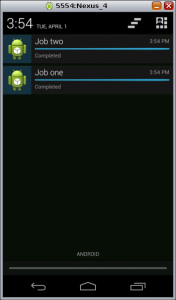

Here you can download the source code of the app.

Leave a Reply